EMG/NCS
What is an EMG?
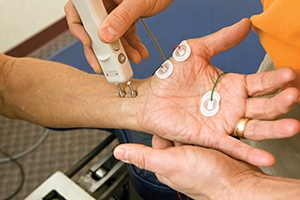 Electrodiagnostic medicine is the study of diseases of nerves and muscles. Your doctor has recommended an Electromyogram (EMG) test to see if your muscles and nerves are working right. You can have problems in only one part of your body or throughout your body. The results of the tests will help your doctor decide what is wrong and how it can be treated.
Electrodiagnostic medicine is the study of diseases of nerves and muscles. Your doctor has recommended an Electromyogram (EMG) test to see if your muscles and nerves are working right. You can have problems in only one part of your body or throughout your body. The results of the tests will help your doctor decide what is wrong and how it can be treated.
Needle EMG
For this part of the test, a small, thin needle is put in several muscles to see if there are any problems. A new needle is used for each patient and it is thrown away after the test. There may be a small amount of pain when the needle is put in. The doctor tests only the muscles necessary to decide what is wrong. The doctor will look at and listen to the electrical signals that travel from the needle to the EMG machine. The doctor then uses his medical knowledge to figure out what could be causing your problem.
What is a NCS?
Nerve Conduction Study (NCS) shows how well the body’s electrical signals are traveling to a nerve. This is done by applying small electrical shocks to the nerve and recording how the nerve works. These shocks cause a quick, mild, tingling feeling. The doctor may test several nerves.
How to prepare for your EMG/NCS
- Take a bath or shower to remove oil from your skin. Do not use body lotion on the day of the test.
- Tell the doctor performing the EMG/NCS if you are taking aspirin, blood thinners (like Coumadin®), have a pacemaker, or have hemophilia. If you have myasthenia gravis, ask the doctor performing the EMG/NCS if you should take Mestinon (pyridostismine) the day of or the day before the test.
Getting the results for EMG/NCS
The doctor who performed the EMG/NCS may discuss your test results with you or send them to your regular doctor. After the exam, check with your regular doctor for the next step in your care.
